Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
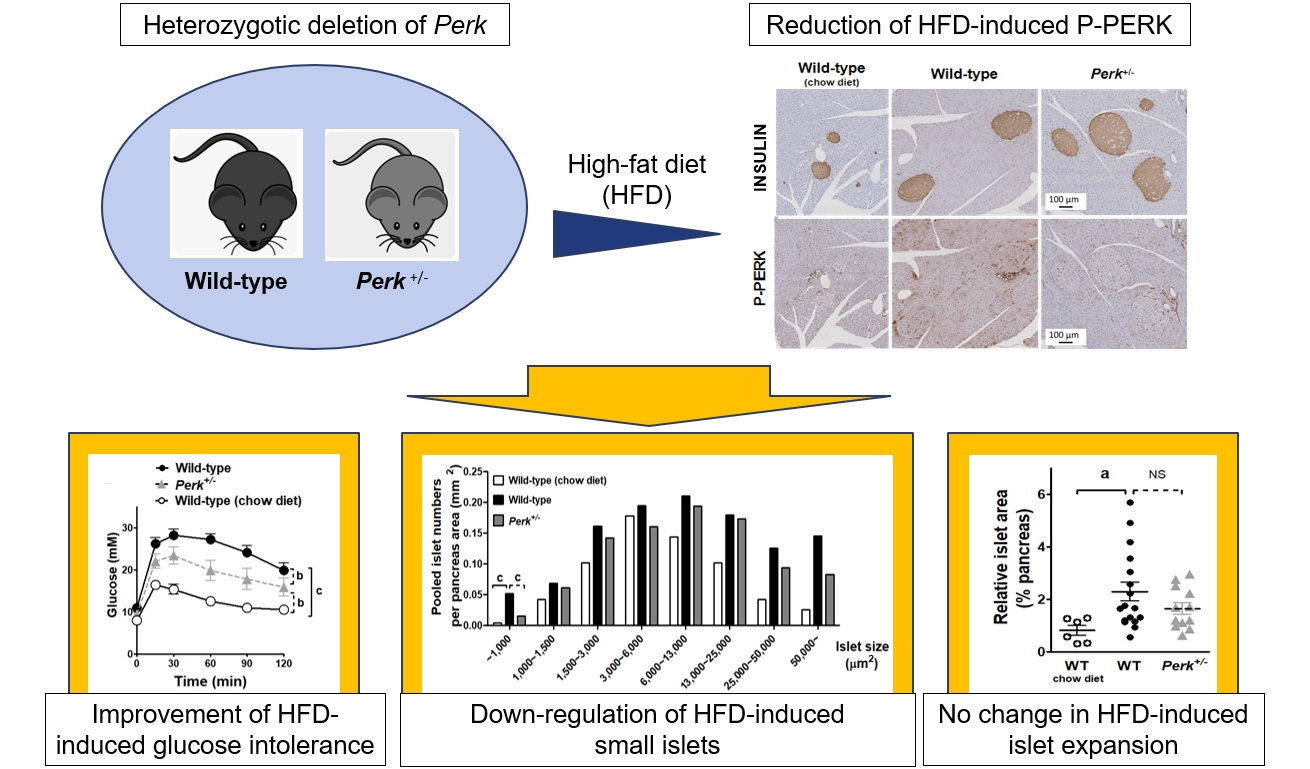
- Partial Deletion of Perk Improved High-Fat Diet-Induced Glucose Intolerance in Mice
- Jooyeop Lee, Min Joo Kim, Seoil Moon, Ji Yoon Lim, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):782-787. Published online November 13, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1738
- 721 View
- 45 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Although pancreatic endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) is indispensable to beta cells, low-dose PERK inhibitor improved glucose- stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) and hyperglycemia in diabetic mice. Current study examined if partial deletion of Perk (Perk+/-) recapitulated the effects of PERK inhibitor, on the contrary to the complete deletion. Perk+/- mice and wild-type controls were fed with a high-fat diet (HFD) for 23 weeks. Glucose tolerance was evaluated along with serum insulin levels and islet morphology. Perk+/- mice on normal chow were comparable to wild-type mice in various metabolic features. HFD-induced obesity was not influenced by Perk reduction; however, HFD-induced glucose intolerance was significantly improved since 15-week HFD. HFD-induced compromises in GSIS were relieved by Perk reduction, accompanied by reductions in phosphorylated PERK and activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) in the islets. Meanwhile, HFD-induced islet expansion was not significantly affected. In summary, partial deletion of Perk improved glucose tolerance and GSIS impaired by diet-induced obesity, without changes in body weights or islet mass.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Triglyceride-Glucose Index Predicts Future Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases: A 16-Year Follow-up in a Prospective, Community-Dwelling Cohort Study
- Joon Ho Moon, Yongkang Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi, Nam H. Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):406-417. Published online August 3, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1703

- 2,670 View
- 166 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
While the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index is a measure of insulin resistance, its association with cardiovascular disease (CVD) has not been well elucidated. We evaluated the TyG index for prediction of CVDs in a prospective large communitybased cohort.
Methods
Individuals 40 to 70 years old were prospectively followed for a median 15.6 years. The TyG index was calculated as the Ln [fasting triglycerides (mg/dL)×fasting glucose (mg/dL)/2]. CVDs included any acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease or cerebrovascular disease. We used a Cox proportional hazards model to estimate CVD risks according to quartiles of the TyG index and plotted the receiver operating characteristics curve for the incident CVD.
Results
Among 8,511 subjects (age 51.9±8.8 years; 47.5% males), 931 (10.9%) had incident CVDs during the follow-up. After adjustment for age, sex, body mass index, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, total cholesterol, smoking, alcohol, exercise, and C-reactive protein, subjects in the highest TyG quartile had 36% increased risk of incident CVD compared with the lowest TyG quartile (hazard ratio, 1.36; 95% confidence interval, 1.10 to 1.68). Carotid plaque, assessed by ultrasonography was more frequent in subjects in the higher quartile of TyG index (P for trend=0.049 in men and P for trend <0.001 in women). The TyG index had a higher predictive power for CVDs than the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (area under the curve, 0.578 for TyG and 0.543 for HOMA-IR). Adding TyG index on diabetes or hypertension alone gave sounder predictability for CVDs.
Conclusion
The TyG index is independently associated with future CVDs in 16 years of follow-up in large, prospective Korean cohort. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting diabetes remission at 3 months after bariatric surgery in patients with obesity combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Kaisheng Yuan, Bing Wu, Ruiqi Zeng, Fuqing Zhou, Ruixiang Hu, Cunchuan Wang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(1): 169. CrossRef - Association between the triglyceride glucose index and chronic total coronary occlusion: A cross-sectional study from southwest China
Kaiyong Xiao, Huili Cao, Bin Yang, Zhe Xv, Lian Xiao, Jianping Wang, Shuiqing Ni, Hui Feng, Zhongwei He, Lei Xv, Juan Li, Dongmei Xv
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(4): 850. CrossRef - The association between TyG and all-cause/non-cardiovascular mortality in general patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is modified by age: results from the cohort study of NHANES 1999–2018
Younan Yao, Bo Wang, Tian Geng, Jiyan Chen, Wan Chen, Liwen Li
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
Min Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Bae, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Mi Sook Yun, Yang Ho Kang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111640. CrossRef - Evaluation of the novel three lipid indices for predicting five- and ten-year incidence of cardiovascular disease: findings from Kerman coronary artery disease risk factors study (KERCADRS)
Alireza Jafari, Hamid Najafipour, Mitra Shadkam, Sina Aminizadeh
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting diabetes remission at 3 months after bariatric surgery in patients with obesity combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus

- Diabetes
- Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes in Koreans
- Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):9-16. Published online March 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.9
- 5,413 View
- 111 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub The pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes is characterized by variable degrees of insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion. Both genetic and environmental factors serve as etiologic factors. Recent genetic studies have identified at least 83 variants associated with diabetes. A significant number of these loci are thought to be involved in insulin secretion, either through β-cell development or β-cell dysfunction. Environmental factors have changed rapidly during the past half century, and the increased prevalence of obesity and diabetes can be attributed to these changes. Environmental factors may affect epigenetic changes and alter susceptibility to diabetes. A recent epidemiologic study revealed that Korean patients with type 2 diabetes already had impaired insulin secretion and insulin resistance 10 years before the onset of diabetes. Those who developed diabetes showed impaired β-cell compensation with an abrupt decrease in insulin secretion during the last 2 years before diabetes developed. The retrograde trajectory of the disposition index differed according to the baseline subgroups of insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity. We hope that obtaining a more detailed understanding of the perturbations in the major pathophysiologic process of diabetes on the individual level will eventually lead to the implementation of precision medicine and improved patient outcomes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Stress-Reducing Psychological Interventions as Adjuvant Therapies for
Diabetic Chronic Wounds
Isadora Pombeiro, João Moura, M. Graça Pereira, Eugénia Carvalho
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Umbilical Cord-Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Improves Insulin Resistance in C2C12 Cell
Kyung-Soo Kim, Yeon Kyung Choi, Mi Jin Kim, Jung Wook Hwang, Kyunghoon Min, Sang Youn Jung, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Soo Choi, Yong-Wook Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 260. CrossRef - Dose-Dependent Effect of Smoking on Risk of Diabetes Remains after Smoking Cessation: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Se Eun Park, Mi Hae Seo, Jung-Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Yang-Hyun Kim, Kyung-Do Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 539. CrossRef - DNA Methylation Changes Associated With Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease in an East Asian Population
Hakyung Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyong Soo Park, Joohon Sung, Soo Heon Kwak
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(10): e3837. CrossRef - Associations among Obesity Degree, Glycemic Status, and Risk of Heart Failure in 9,720,220 Korean Adults
Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Yang-Hyun Kim, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 592. CrossRef - Smoking as a Target for Prevention of Diabetes
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 402. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics of diabetic ketoacidosis in users and non-users of SGLT2 inhibitors
J.Y. Jeon, S.-K. Kim, K.-S. Kim, S.O. Song, J.-S. Yun, B.-Y. Kim, C.-H. Kim, S.O. Park, S. Hong, D.H. Seo, J.A. Seo, J.H. Noh, D.J. Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2019; 45(5): 453. CrossRef - Identifying Pathogenic Variants of Monogenic Diabetes Using Targeted Panel Sequencing in an East Asian Population
Seung Shin Park, Se Song Jang, Chang Ho Ahn, Jung Hee Kim, Hye Seung Jung, Young Min Cho, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Jong Hee Chae, Jae Hyun Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Hak C Jang, Jee Cheol Bae, Jong Cheol Won, Sung-Hoon Kim, Jong-Il Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 104(9): 4188. CrossRef - Epigenetic Markers and Microbiota/Metabolite-Induced Epigenetic Modifications in the Pathogenesis of Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, Type 2 Diabetes, and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Daniela Stols-Gonçalves, Luca Schiliró Tristão, Peter Henneman, Max Nieuwdorp
Current Diabetes Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The cut-off values of surrogate measures for insulin resistance in the Korean population according to the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KOGES)
Bongyoung Kim, Hyun Young Choi, Wonhee Kim, Chiwon Ahn, Juncheol Lee, Jae Guk Kim, Jihoon Kim, Hyungoo Shin, Jae Myung Yu, Shinje Moon, Taulant Muka
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(11): e0206994. CrossRef
- Stress-Reducing Psychological Interventions as Adjuvant Therapies for
Diabetic Chronic Wounds

- Erratum: Correction of Figure. Clinical Implications of Various Criteria for the Biochemical Diagnosis of Insulinoma
- Chang Ho Ahn, Lee-Kyung Kim, Jie Eun Lee, Chan-Hyeon Jung, Se-Hee Min, Kyong Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim, Young Min Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(2):306. Published online June 23, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.306
- 2,863 View
- 31 Download

- Clinical Study
- 1,5-Anhydro-D-Glucitol Could Reflect Hypoglycemia Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Receiving Insulin Therapy
- Min Kyeong Kim, Hye Seung Jung, Soo Heon Kwak, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(2):284-291. Published online May 27, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.2.284
- 4,376 View
- 41 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The identification of a marker for hypoglycemia could help patients achieve strict glucose control with a lower risk of hypoglycemia. 1,5-Anhydro-D-glucitol (1,5-AG) reflects postprandial hyperglycemia in patients with well-controlled diabetes, which contributes to glycemic variability. Because glycemic variability is related to hypoglycemia, we aimed to evaluate the value of 1,5-AG as a marker of hypoglycemia.
Methods We enrolled 18 adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) receiving insulin therapy and assessed the occurrence of hypoglycemia within a 3-month period. We measured 1,5-AG level, performed a survey to score the severity of hypoglycemia, and applied a continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS).
Results 1,5-AG was significantly lower in the high hypoglycemia-score group compared to the low-score group. Additionally, the duration of insulin treatment was significantly longer in the high-score group. Subsequent analyses were adjusted by the duration of insulin treatment and mean blood glucose, which was closely associated with both 1,5-AG level and hypoglycemia risk. In adjusted correlation analyses, 1,5-AG was negatively correlated with hypoglycemia score, area under the curve at 80 mg/dL, and low blood glucose index during CGMS (
P =0.068,P =0.033, andP =0.060, respectively).Conclusion 1,5-AG level was negatively associated with hypoglycemia score determined by recall and with documented hypoglycemia after adjusting for mean glucose and duration of insulin treatment. As a result, this level could be a marker of the risk of hypoglycemia in patients with well-controlled T2DM receiving insulin therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mobile Healthcare System Provided by Primary Care Physicians Improves Quality of Diabetes Care
Tae Jung Oh, Jie-Eun Lee, Seok Kim, Sooyoung Yoo, Hak Chul Jang
CardioMetabolic Syndrome Journal.2021; 1(1): 88. CrossRef - Effects of mobile phone application combined with or without self‐monitoring of blood glucose on glycemic control in patients with diabetes: A randomized controlled trial
Yuan Yu, Qun Yan, Huizhi Li, Hongmei Li, Lin Wang, Hua Wang, Yiyun Zhang, Lei Xu, Zhaosheng Tang, Xinfeng Yan, Yinghua Chen, Huili He, Jie Chen, Bo Feng
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2019; 10(5): 1365. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - A Diet Diverse in Bamboo Parts is Important for Giant Panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) Metabolism and Health
Hairui Wang, Heju Zhong, Rong Hou, James Ayala, Guangmang Liu, Shibin Yuan, Zheng Yan, Wenping Zhang, Yuliang Liu, Kailai Cai, Zhigang Cai, He Huang, Zhihe Zhang, De Wu
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Low and exacerbated levels of 1,5-anhydroglucitol are associated with cardiovascular events in patients after first-time elective percutaneous coronary intervention
Shuhei Takahashi, Kazunori Shimada, Katsumi Miyauchi, Tetsuro Miyazaki, Eiryu Sai, Manabu Ogita, Shuta Tsuboi, Hiroshi Tamura, Shinya Okazaki, Tomoyuki Shiozawa, Shohei Ouchi, Tatsuro Aikawa, Tomoyasu Kadoguchi, Hamad Al Shahi, Takuma Yoshihara, Makoto Hi
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
- Mobile Healthcare System Provided by Primary Care Physicians Improves Quality of Diabetes Care

- Endocrine Research
- Thyroid Hormone Regulates the mRNA Expression of Small Heterodimer Partner through Liver Receptor Homolog-1
- Hwa Young Ahn, Hwan Hee Kim, Ye An Kim, Min Kim, Jung Hun Ohn, Sung Soo Chung, Yoon-Kwang Lee, Do Joon Park, Kyong Soo Park, David D. Moore, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(4):584-592. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.584
- 3,764 View
- 39 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Expression of hepatic cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) is negatively regulated by orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner (SHP). In this study, we aimed to find whether thyroid hormone regulates SHP expression by modulating the transcriptional activities of liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1).
Methods We injected thyroid hormone (triiodothyronine, T3) to C57BL/6J wild type. RNA was isolated from mouse liver and used for microarray analysis and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Human hepatoma cell and primary hepatocytes from mouse liver were used to confirm the effect of T3
in vitro . Promoter assay and electrophoretic mobility-shift assay (EMSA) were also performed using human hepatoma cell lineResults Initial microarray results indicated that SHP expression is markedly decreased in livers of T3 treated mice. We confirmed that T3 repressed SHP expression in the liver of mice as well as in mouse primary hepatocytes and human hepatoma cells by real-time PCR analysis. LRH-1 increased the promoter activity of SHP; however, this increased activity was markedly decreased after thyroid hormone receptor β/retinoid X receptor α/T3 administration. EMSA revealed that T3 inhibits specific LRH-1 DNA binding.
Conclusion We found that thyroid hormone regulates the expression of SHP mRNA through interference with the transcription factor, LRH-1.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bile acid and receptors: biology and drug discovery for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Ting-ying Jiao, Yuan-di Ma, Xiao-zhen Guo, Yun-fei Ye, Cen Xie
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2022; 43(5): 1103. CrossRef - Loperamide induces excessive accumulation of bile acids in the liver of mice with different diets
Zili Lei, Hedong Rong, Yanhong Yang, Siping Yu, Tianle Zhang, Lei Chen, Ya Nie, Qi Song, Qing Hu, Jiao Guo
Toxicology.2022; 477: 153278. CrossRef - Pathogenesis of hypothyroidism-induced NAFLD is driven by intra- and extrahepatic mechanisms
Giuseppe Ferrandino, Rachel R. Kaspari, Olga Spadaro, Andrea Reyna-Neyra, Rachel J. Perry, Rebecca Cardone, Richard G. Kibbey, Gerald I. Shulman, Vishwa Deep Dixit, Nancy Carrasco
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Bile acid and receptors: biology and drug discovery for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease

- Clinical Study
- Clinical Characteristics of Subjects with Sulfonylurea-Dependent Type 2 Diabetes
- Se Hee Min, Soo Heon Kwak, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(4):509-513. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.509
- 4,491 View
- 69 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Even though several oral anti-diabetic drugs (OAD) with various modes of action are replacing sulfonylurea (SU), some patients seem to be dependent on SU for adequate glycemic control. Therefore, we evaluated the clinical characteristics of such patients.
Methods We selected the patients with type 2 diabetes who met following criteria from 2009 to 2014 at Seoul National University Hospital: glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) was maintained below 7.5% for at least 6 months under small dose of SU (glimepiride ≤2 mg/day or equivalent dose); after discontinuation of SU, HbA1c increased ≥1.2% within 3 months or ≥1.5% within 6 months; and after resuming SU, HbA1c reduction was ≥0.8% or reduction of fasting plasma glucose was ≥40 mg/dL within 3 months. Patients with impaired hepatic or renal function, and steroid users were excluded.
Results Nineteen subjects were enrolled: after averaged 4.8±1.5 months of SU-free period, HbA1c increased from 6.7%±0.4% to 8.8%±0.8% even though adding other OAD such as gliptins. However, HbA1c decreased to 7.4%±0.7% after resuming SU within 2.4±0.8 months. There was no sexual predominance. Despite their old age (67±11 years) and long duration of diabetes (18±10 years), fasting C-peptide was relatively well-reserved (3.9±2.6 ng/mL), and nephropathy was not observed (albumin-creatinine ratio 21.2±16.6 mg/g and estimated glomerular filtration rate 75.8±18.0 mL/min/1.73 m2). Strong family history was also noted (73.7%).
Conclusion Despite hypoglycemia risk of SU, it seemed indispensable for a subset of patients with regard to insulin secretion. Genetic influences would be evaluated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incident Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Patients Treated with a Sulfonylurea: A Nationwide, Nested, Case-Control Study
Ji-Yeon Lee, Suk-Yong Jang, Chung Mo Nam, Eun Seok Kang
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A genetic variant in GLP1R is associated with response to DPP-4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes
Eugene Han, Hye Sun Park, Obin Kwon, Eun Yeong Choe, Hye Jin Wang, Yong-ho Lee, Sang-Hak Lee, Chul Hoon Kim, Lee-Kyung Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park, Chul Sik Kim, Eun Seok Kang
Medicine.2016; 95(44): e5155. CrossRef
- Incident Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk in Patients Treated with a Sulfonylurea: A Nationwide, Nested, Case-Control Study

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Genetic Studies on Diabetic Microvascular Complications: Focusing on Genome-Wide Association Studies
- Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(2):147-158. Published online June 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.2.147
- 4,248 View
- 39 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Diabetes is a common metabolic disorder with a worldwide prevalence of 8.3% and is the leading cause of visual loss, end-stage renal disease and amputation. Recently, genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have identified genetic risk factors for diabetic microvascular complications of retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy. We summarized the recent findings of GWASs on diabetic microvascular complications and highlighted the challenges and our opinion on future directives. Five GWASs were conducted on diabetic retinopathy, nine on nephropathy, and one on neuropathic pain. The majority of recent GWASs were underpowered and heterogeneous in terms of study design, inclusion criteria and phenotype definition. Therefore, few reached the genome-wide significance threshold and the findings were inconsistent across the studies. Recent GWASs provided novel information on genetic risk factors and the possible pathophysiology of diabetic microvascular complications. However, further collaborative efforts to standardize phenotype definition and increase sample size are necessary for successful genetic studies on diabetic microvascular complications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Genetics of diabetes
Shiwali Goyal, Jyoti Rani, Mohd Akbar Bhat, Vanita Vanita
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(6): 656. CrossRef - Plasma thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor and the 1040C/T polymorphism are risk factors for diabetic kidney disease in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes
Qinghua Huang, Dujin Feng, Lianlian Pan, Huan Wang, Yan Wu, Bin Zhong, Jianguang Gong, Huijun Lin, Xianming Fei
PeerJ.2023; 11: e16352. CrossRef - The G Allele of the rs12050217 Polymorphism in the BDKRB1 Gene Is Associated with Protection for Diabetic Retinopathy
Leticia A. Brondani, Daisy Crispim, Julia Pisco, Jorge A. Guimarães, Markus Berger
Current Eye Research.2019; 44(9): 994. CrossRef - Genome‐wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for diabetic nephropathy in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Kyung H. Jeong, Jin S. Kim, Jeong‐Taek Woo, Sang Y. Rhee, Yu H. Lee, Yang G. Kim, Ju‐Young Moon, Su K. Kim, Sun W. Kang, Sang H. Lee, Yeong H. Kim
Clinical Genetics.2019; 96(1): 35. CrossRef - Diabetic polyneuropathy, deep white matter lesions, and carotid atherosclerosis: is there any association?
Sevgi Ferik, Hayat Güven, Mehlika Panpallı Ateş, Işık Conkbayır, Selçuk Çomoğlu, Bülent Güven
Neurological Sciences.2018; 39(1): 103. CrossRef - Altered expression of WFS1 and NOTCH2 genes associated with diabetic nephropathy in T2DM patients
Sahar A. Sharaf, Nagwa A. Kantoush, Dina F. Ayoub, Alshaymaa A. Ibrahim, Amaal A. Abdelaal, Rokaya Abdel Aziz, Mahmoud M. ElHefnawi, Amira N. Ahmed
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 140: 304. CrossRef - Precision medicine in diabetes prevention, classification and management
Fangying Xie, Juliana CN Chan, Ronald CW Ma
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2018; 9(5): 998. CrossRef - Clinical worthlessness of genetic prediction of common forms of diabetes mellitus and related chronic complications
R. Buzzetti, S. Prudente, M. Copetti, M. Dauriz, S. Zampetti, M. Garofolo, G. Penno, V. Trischitta
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2017; 27(2): 99. CrossRef - Diabetic macular oedema: clinical risk factors and emerging genetic influences
Ebony Liu, Jamie E Craig, Kathryn Burdon
Clinical and Experimental Optometry.2017; 100(6): 569. CrossRef - Normoalbuminuric diabetic kidney disease
Chao Chen, Chang Wang, Chun Hu, Yachun Han, Li Zhao, Xuejing Zhu, Li Xiao, Lin Sun
Frontiers of Medicine.2017; 11(3): 310. CrossRef - Biomarkers of Diabetic Retinopathy
Daniel Shu Wei Ting, Kara-Anne Tan, Val Phua, Gavin Siew Wei Tan, Chee Wai Wong, Tien Yin Wong
Current Diabetes Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Heme Oxygenase-1 Promoter Polymorphisms and the Development of Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes
Eun Young Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Soo Hyun Kim, Kyu Sik Jung, Obin Kwon, Beom Seok Kim, Chung Mo Nam, Chun Sik Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Medicine.2015; 94(43): e1825. CrossRef
- Genetics of diabetes

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Mitochondrial Complexes I and II Are More Susceptible to Autophagy Deficiency in Mouse β-Cells
- Min Joo Kim, Ok Kyong Choi, Kyung Sil Chae, Min Kyeong Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Masaaki Komatsu, Keiji Tanaka, Hakmo Lee, Sung Soo Chung, Soo Heon Kwak, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(1):65-70. Published online March 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.1.65
- 3,954 View
- 40 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Damaged mitochondria are removed by autophagy. Therefore, impairment of autophagy induces the accumulation of damaged mitochondria and mitochondrial dysfunction in most mammalian cells. Here, we investigated mitochondrial function and the expression of mitochondrial complexes in autophagy-related 7 (
Atg7 )-deficient β-cells.Methods To evaluate the effect of autophagy deficiency on mitochondrial function in pancreatic β-cells, we isolated islets from
Atg7 F/F:RIP-Cre + mice and wild-type littermates. Oxygen consumption rate and intracellular adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) content were measured. The expression of mitochondrial complex genes inAtg7 -deficient islets and in β-TC6 cells transfected with siAtg7 was measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.Results Baseline oxygen consumption rate of
Atg7 -deficient islets was significantly lower than that of control islets (P <0.05). Intracellular ATP content ofAtg7 -deficient islets during glucose stimulation was also significantly lower than that of control islets (P <0.05). By Oxygraph-2k analysis, mitochondrial respiration inAtg7 -deficient islets was significantly decreased overall, although state 3 respiration and responses to antimycin A were unaffected. The mRNA levels of mitochondrial complexes I, II, III, and V inAtg7 -deficient islets were significantly lower than in control islets (P <0.05). Down-regulation ofAtg7 in β-TC6 cells also reduced the expression of complexes I and II, with marginal significance (P <0.1).Conclusion Impairment of autophagy in pancreatic β-cells suppressed the expression of some mitochondrial respiratory complexes, and may contribute to mitochondrial dysfunction. Among the complexes, I and II seem to be most vulnerable to autophagy deficiency.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Proteomic pathways to metabolic disease and type 2 diabetes in the pancreatic islet
Belinda Yau, Sheyda Naghiloo, Alexis Diaz-Vegas, Austin V. Carr, Julian Van Gerwen, Elise J. Needham, Dillon Jevon, Sing-Young Chen, Kyle L. Hoehn, Amanda E. Brandon, Laurence Macia, Gregory J. Cooney, Michael R. Shortreed, Lloyd M. Smith, Mark P. Keller,
iScience.2021; 24(10): 103099. CrossRef - Natural compound oblongifolin C inhibits autophagic flux, and induces apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in human cholangiocarcinoma QBC939 cells
Aiqing Zhang, Wei He, Huimin Shi, Xiaodan Huang, Guozhong Ji
Molecular Medicine Reports.2016; 14(4): 3179. CrossRef - Autophagy deficiency in β cells blunts incretin-induced suppression of glucagon release from α cells
Min Joo Kim, Ok Kyong Choi, Kyung Sil Chae, Hakmo Lee, Sung Soo Chung, Dong-Sik Ham, Ji-Won Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
Islets.2015; 7(5): e1129096. CrossRef
- Proteomic pathways to metabolic disease and type 2 diabetes in the pancreatic islet

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Clinical Implications of Various Criteria for the Biochemical Diagnosis of Insulinoma
- Chang Ho Ahn, Lee-Kyung Kim, Jie Eun Lee, Chan-Hyeon Jung, Se-Hee Min, Kyong Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim, Young Min Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):498-504. Published online December 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.498
- 4,419 View
- 74 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Among the various diagnostic criteria for insulinoma, the ratio criteria have been controversial. However, the amended insulin-glucose ratio exhibited excellent diagnostic performance in a recent retrospective cohort study, although it has not yet been validated in other patient cohorts. We examined the diagnostic performance of the current criteria of the Endocrine Society, insulin-glucose ratio, C-peptide-glucose ratio, and amended ratios in terms of differentiating insulinomas.
Methods We reviewed the medical records of patients who underwent evaluation for hypoglycemia from 2000 to 2013. Fourteen patients with histopathologically confirmed insulinoma and 18 patients without clinical evidence of insulinoma were included. The results of a prolonged fast test were analyzed according to the abovementioned criteria.
Results Fulfilling all three Endocrine Society criteria-plasma levels of glucose (<3.0 mmol/L), insulin (≥8 pmol/L), and C-peptide (≥0.2 nmol/L)-exhibited 100% sensitivity and 89% specificity. Fulfilling the glucose and C-peptide criteria showed 100% sensitivity and 83% specificity, while fulfilling the glucose and insulin criteria showed 100% sensitivity and 72% specificity. Among the ratio criteria, the insulin-glucose ratio [>24.0 (pmol/L)/(mmol/L)] gave the highest area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, with 93% sensitivity and 94% specificity.
Conclusion Fulfilling the glucose, insulin, and C-peptide criteria of the Endocrine Society guidelines exhibited the best diagnostic performance for insulinoma. Nonetheless, the insulin-glucose ratio may still have a role in the biochemical diagnosis of insulinoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Homeostasis Model Assessment of β-Cell Function for Diagnosis of Insulinoma
Kálmán Bódis, Martin Schön, Laura Dauben, Miriam Wilker, Klaus Strassburger, Volker Burkart, Michael Roden, Karsten Müssig
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1125. CrossRef - A novel diagnostic model for insulinoma
Feng Wang, Zhe Yang, XiuBing Chen, Yiling Peng, HaiXing Jiang, ShanYu Qin
Discover Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of the current guidelines for detecting insulinoma
Laura Dauben, Marie-Christine Simon, Klaus Strassburger, Volker Burkart, Katharina S Weber, Sven Schinner, Michael Roden, Karsten Müssig
European Journal of Endocrinology.2019; 180(6): 381. CrossRef - EUS-guided lauromacrogol ablation of insulinomas: a novel treatment
Shanyu Qin, Yongru Liu, Hongjian Ning, Lin Tao, Wei Luo, Donghong Lu, Zuojie Luo, Yingfen Qin, Jia Zhou, Junqiang Chen, Haixing Jiang
Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology.2018; 53(5): 616. CrossRef - Diagnosis of insulinoma using the ratios of serum concentrations of insulin and C-peptide to glucose during a 5-hour oral glucose tolerance test
Xu Li, Feng Zhang, Haibing Chen, Haoyong Yu, Jian Zhou, Ming Li, Qing Li, Lianxi Li, Jun Yin, Fang Liu, Yuqian Bao, Junfeng Han, Weiping Jia
Endocrine Journal.2017; 64(1): 49. CrossRef - Insulinoma in a 5‐Year‐Old Dexter Cow
C. Binici, S. Plog, O. Kershaw, M. Schmicke, J.H. van der Kolk, K.E. Müller
Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine.2016; 30(4): 1402. CrossRef - Vague neuroglycopenic complaints camouflage diagnosis of adolescent insulinoma: a case report
Kelsee Halpin, Ryan McDonough, Patria Alba, Jared Halpin, Vivekanand Singh, Yun Yan
International Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Homeostasis Model Assessment of β-Cell Function for Diagnosis of Insulinoma

- Obesity and Metabolism
- A Novel Mutation in the Von Hippel-Lindau Tumor Suppressor Gene Identified in a Patient Presenting with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Yun Hyi Ku, Chang Ho Ahn, Chan-Hyeon Jung, Jie Eun Lee, Lee-Kyung Kim, Soo Heon Kwak, Hye Seung Jung, Kyong Soo Park, Young Min Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(4):320-325. Published online December 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.4.320
- 3,562 View
- 29 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease is an autosomal dominantly inherited, multisystemic tumor syndrome caused by mutations in the
VHL gene. To date, more than 1,000 germline and somatic mutations of theVHL gene have been reported. We present a novel mutation in theVHL tumor suppressor gene that presented with gestational diabetes mellitus.Methods A 30-year-old woman presented with gestational diabetes mellitus. She sequentially showed multiple pancreatic cysts, spinal cord hemangioblastoma, cerebellar hemangioblastoma, and clear cell type renal cell carcinomas. Also, her father and brother had brain hemangioblastomas. Each of the three exons of the
VHL gene was individually amplified by polymerase chain reaction and direct sequencing was performed using an ABI 3730 DNA analyzer.Results DNA sequence analysis to determine the presence of
VHL mutation in her family revealed del291C, a novel frameshift mutation.Conclusion We found a novel mutation in the
VHL tumor suppressor gene that presented with gestational diabetes mellitus.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diversities of Mechanism in Patients with VHL Syndrome and diabetes: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review
Yanlei Wang, Zhaoxiang Liu, Wenhui Zhao, Chenxiang Cao, Luqi Xiao, Jianzhong Xiao
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2024; Volume 17: 1611. CrossRef - Retinal hemangioblastoma in a patient with Von Hippel-Lindau disease: A case report and literature review
Yikeng Huang, Weiwen Hu, Xionggao Huang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Updates on the Role of Molecular Alterations and NOTCH Signalling in the Development of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms
Claudia von Arx, Monica Capozzi, Elena López-Jiménez, Alessandro Ottaiano, Fabiana Tatangelo, Annabella Di Mauro, Guglielmo Nasti, Maria Lina Tornesello, Salvatore Tafuto
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(9): 1277. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef
- Diversities of Mechanism in Patients with VHL Syndrome and diabetes: A Report of Two Cases and Literature Review

- Thyroid
- Expression of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor mRNA in Mouse C2C12 Skeletal Muscle Cells
- Jung Hun Ohn, Sun Kyoung Han, Do Joon Park, Kyong Soo Park, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(2):119-124. Published online June 18, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.2.119
- 3,488 View
- 39 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We analyzed whether thyroid stimulating hormone receptor (TSH-R) is expressed in a skeletal muscle cell line and if TSH has influence on the differentiation of muscle cells or on the determination of muscle fiber types.
Methods TSH-R gene expression was detected with nested real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in C2C12, a mouse skeletal muscle cell line. The effect of TSH on myotube differentiation was assessed by microscopic examination of myotube formation and through the measurement of expression of muscle differentiation markers, i.e., myogenin and myoD, and muscle type-specific genes, i.e., MyHC1, MyHC2a, and MyHC2b, with quantitative RT-PCR before and after incubation of C2C12 myotube with TSH.
Results TSH-R was expressed in the mouse skeletal muscle cell line. However, treatment with TSH had little effect on the differentiation of muscle cells, although the expression of the muscle differention marker myogenin was significantly increased after TSH treatment. Treatment of TSH did not affect the expression of muscle type-specific genes.
Conclusion TSH-R is expressed in a mouse skeletal muscle cell line, but the role of TSH receptor signaling in skeletal muscle needs further investigation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations between thyroid hormones and appendicular skeletal muscle index, and hand grip strength in people with diabetes: The KAMOGAWA-A study
Shinnosuke Hata, Hiroshi Okada, Megumi Minamida, Junya Hironaka, Yuka Hasegawa, Yuriko Kondo, Hanako Nakajima, Nobuko Kitagawa, Takuro Okamura, Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Takafumi Osaka, Noriyuki Kitagawa, Saori Majima, Takafumi Senmaru, Emi Ushigome, Naoko Nak
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111573. CrossRef - Clinical parameters correlated with the psoas muscle index in Japanese individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Emi Asano-Hayami, Yoshiaki Morishita, Tomohide Hayami, Yuka Shibata, Toshiki Kiyose, Sachiko Sasajima, Yusuke Hayashi, Mikio Motegi, Makoto Kato, Saeko Asano, Hiromi Nakai-Shimoda, Yuichiro Yamada, Emiri Miura-Yura, Tatsuhito Himeno, Masaki Kondo, Shin Ts
Diabetology International.2023; 14(1): 76. CrossRef - Effect of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Suppression on Muscle Function After Total Thyroidectomy in Patients With Thyroid Cancer
Jun Choul Lee, Byong-Sop Song, Young Mi Kang, Yu-Ri Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Ju Hee Lee, Minho Shong, Hyon-Seung Yi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Different Relationships Between Thyrotropin and Muscle Strength According to Sex and Age in Euthyroid Koreans (The 6th Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey 2014–2015)
Seong Hee Ahn, Da Hea Seo, Yongin Cho, Mihye Jung, So Hun Kim, Seongbin Hong
Thyroid.2020; 30(12): 1710. CrossRef - A Significant Association of Upper Limb Muscle Strength with Thyroid Function in Overweight and Obese Population: A Study of the Sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES 2014-2015)
Jeongmin Lee, Kwanhoon Jo, Jeonghoon Ha, Dong-Jun Lim, Jung Min Lee, Sang-Ah Chang, Moo Il Kang, Min-Hee Kim, Flavia Magri
International Journal of Endocrinology.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Muscle-derived IL-6 improved insulin resistance of C2C12 cells through activating AMPK and inhibiting p38MAPK signal pathway in vitro
Hui Tang, Shuai Deng, Jian-guang Cai, Xue-nan Ma, Man Liu, Liang Zhou
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2019; 39(3): 486. CrossRef - Thyroid Function as a Predictor of Handgrip Strength Among Middle-Aged and Older Euthyroid Adults: The TCLSIH Cohort Study
Yeqing Gu, Ge Meng, Hongmei Wu, Qing Zhang, Li Liu, Xue Bao, Yawen Wang, Shunming Zhang, Shaomei Sun, Xing Wang, Ming Zhou, Qiyu Jia, Kun Song, Kaijun Niu
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2019; 20(10): 1236. CrossRef - Association of Serum TSH With Handgrip Strength in Community-Dwelling Euthyroid Elderly
Beom-Jun Kim, Seung Hun Lee, Carlos M Isales, Mark W Hamrick, Mi Kyung Kwak, Jung-Min Koh
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2018; 103(11): 3986. CrossRef - Changes in Thyroid Hormone Levels Within the Normal and/or Subclinical Hyper- or Hypothyroid Range Do Not Affect Circulating Irisin Levels in Humans
Grigorios Panagiotou, Kalliopi Pazaitou-Panayiotou, Stavroula A. Paschou, Despina Komninou, Nikolaos Kalogeris, Andromachi Vryonidou, Christos S. Mantzoros
Thyroid.2016; 26(8): 1039. CrossRef - Thyroid-stimulating hormone improves insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle cells via cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway-dependent upregulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 expression
Min Kyong Moon, Geun Hyung Kang, Hwan Hee Kim, Sun Kyoung Han, Young Do Koo, Sun Wook Cho, Ye An Kim, Byung-Chul Oh, Do Joon Park, Sung Soo Chung, Kyong Soo Park, Young Joo Park
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2016; 436: 50. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef
- Associations between thyroid hormones and appendicular skeletal muscle index, and hand grip strength in people with diabetes: The KAMOGAWA-A study

- Thyroid
- Two Cases of Methimazole-Induced Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome in Graves' Disease
- Eun Roh, Ye An Kim, Eu Jeong Ku, Jae Hyun Bae, Hye Mi Kim, Young Min Cho, Young Joo Park, Kyong Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim, Soo Heon Kwak
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(1):55-60. Published online March 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.1.55
- 6,381 View
- 71 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader We report here the cases of two females with Graves' disease who developed insulin autoimmune syndrome after treatment with methimazole. The patients exhibited a sudden altered mental state after treatment with methimazole for approximately 4 weeks. Patients had hypoglycemia with serum glucose below 70 mg/dL, and laboratory findings showed both high levels of serum insulin and high titers of insulin autoantibodies. The two women had never been exposed to insulin or oral antidiabetic agents, and there was no evidence of insulinoma in imaging studies. After glucose loading, serum glucose, and total insulin levels increased abnormally. One of the patient was found to have HLA-DRB1*0406, which is known to be strongly associated with methimazole-induced insulin autoimmune syndrome. After discontinuation of methimazole, hypoglycemic events disappeared within 1 month. Insulin autoantibody titer and insulin levels decreased within 5 months and there was no further development of hypoglycemic events. We present these cases with a review of the relevant literature.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome: A Systematic Review
MingXu Lin, YuHua Chen, Jie Ning, Tatsuya Kin
International Journal of Endocrinology.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Safety of Antithyroid Drugs in Avoiding Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia in Patients With Graves’ Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Literature Review
Yu-Shan Hsieh
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Case report: hypoglycemia secondary to methimazole-induced insulin autoimmune syndrome in young Taiwanese woman with Graves’ disease
Hsuan-Yu Wu, I-Hua Chen, Mei-Yueh Lee
Medicine.2022; 101(25): e29337. CrossRef - Analysis of the clinical characteristics of insulin autoimmune syndrome induced by methimazole
Linli Sun, Weijin Fang, Dan Yi, Wei Sun, Chunjiang Wang
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2021; 46(2): 470. CrossRef - Preoperative plasmapheresis experience in Graves’ disease patients with anti-thyroid drug-induced hepatotoxicity
Tugce Apaydın, Onur Elbasan, Dilek Gogas Yavuz
Transfusion and Apheresis Science.2020; 59(5): 102826. CrossRef - Glycemic variation in uncontrolled Graves’ disease patients with normal glucose metabolism: Assessment by continuous glucose monitoring
Gu Gao, Feng-fei Li, Yun Hu, Reng-na Yan, Bing-li Liu, Xiao-mei Liu, Xiao-fei Su, Jian-hua Ma, Gang Hu
Endocrine.2019; 64(2): 265. CrossRef - Insulin autoimmune syndrome induced by exogenous insulin injection: a four-case series
Yimin Shen, Xiaoxiao Song, Yuezhong Ren
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment and Management of Anti-Insulin Autoantibodies in Varying Presentations of Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome
David Church, Luís Cardoso, Richard G Kay, Claire L Williams, Bernard Freudenthal, Catriona Clarke, Julie Harris, Myuri Moorthy, Efthmia Karra, Fiona M Gribble, Frank Reimann, Keith Burling, Alistair J K Williams, Alia Munir, T Hugh Jones, Dagmar Führer,
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2018; 103(10): 3845. CrossRef - MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Pathogenesis and management of hypoglycemia
Nana Esi Kittah, Adrian Vella
European Journal of Endocrinology.2017; 177(1): R37. CrossRef - Insulin autoimmune syndrome during the administration of clopidogrel
Eijiro Yamada, Shuichi Okada, Tsugumichi Saito, Aya Osaki, Atushi Ozawa, Masanobu Yamada
Journal of Diabetes.2016; 8(4): 588. CrossRef - Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia associated with insulin antibodies caused by exogenous insulin analog
Chih-Ting Su, Yi-Chun Lin
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism Case Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-tuberculosis Treatment-Induced Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome
Jung Suk Han, Han Ju Moon, Jin Seo Kim, Hong Il Kim, Cheol Hyeon Kim, Min Joo Kim
The Ewha Medical Journal.2016; 39(4): 122. CrossRef - 2016 American Thyroid Association Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Hyperthyroidism and Other Causes of Thyrotoxicosis
Douglas S. Ross, Henry B. Burch, David S. Cooper, M. Carol Greenlee, Peter Laurberg, Ana Luiza Maia, Scott A. Rivkees, Mary Samuels, Julie Ann Sosa, Marius N. Stan, Martin A. Walter
Thyroid.2016; 26(10): 1343. CrossRef - Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome in a Patient with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
In Wook Song, Eugene Han, Nan Hee Cho, Ho Chan Cho
Journal of Korean Thyroid Association.2014; 7(2): 180. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef
- Insulin Autoimmune Syndrome: A Systematic Review

- Primary Hyperaparathyroidism due to Cystic Parathyroid Adenoma not Detected on 99mTc-Sestamibi Scan.
- Ah Reum Khang, Eun Ki Kim, Eun Young Nam, Sun Ju Byeon, Jung Hee Kim, Jung Hun Ohn, Eun Shil Hong, Hyung Jin Choi, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Myung Whun Sung, Chan Soo Shin, Kyong Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(1):83-88. Published online March 1, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.1.83
- 41,911 View
- 30 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Parathyroid cysts, which can be divided into functional and non-functional cysts, are rare causes of primary hyperparathyroidism. A technetium-99m-methoxyisobutylisonitrile (99mTc-sestamibi) parathyroid scan is a sensitive diagnostic tool for the localization, although it sometimes shows a false-negative result. Here we report a case of presumed cystic parathyroid adenoma based on clinical findings and analysis of cystic fluid with negative findings in a parathyroid scan. A 44-year-old male patient visited the hospital due to leg pain and compressive symptoms (dysphagia, hoarseness) that had started 4-5 months before. His serum calcium level was 14.4 mg/dL and his intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) had increased to 478.1 pg/mL. On neck computed tomography, a cystic nodule measuring 6.2 cm was detected in the inferior part of the right thyroid gland. Sestamibi uptake for this nodule was not detected on 2-h delayed imaging, and fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography showed only subtle uptake. Fine-needle aspiration was performed and intracystic iPTH had increased to 61,600 pg/mL. Focused parathyroidectomy guided by intraoperative iPTH monitoring led to successful enucleation of the right inferior parathyroid gland. A parathyroid adenoma was confirmed, and his laboratory results had normalized. This study shows that cystic parathyroid adenoma can sometimes be difficult to detect on a 99mTc-sestamibi parathyroid scan.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Functional parathyroid cystic adenoma: A rare cause of hypercalcemic crisis with primary hyperparathyroidism
BS Sumana, M Sabaretnam, Vijaya Sarathi, Akshatha Savith
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2015; 58(4): 487. CrossRef - Normocalcemic primary hyperparathyroidism: long-term follow-up associated with multiple adenomas
Larissa Pimentel, Sirley Portela, Alyne Loureiro, Francisco Bandeira
Arquivos Brasileiros de Endocrinologia & Metabologia.2014; 58(5): 583. CrossRef
- Functional parathyroid cystic adenoma: A rare cause of hypercalcemic crisis with primary hyperparathyroidism

- Androgen Receptor Gene CAG Repeat Polymorphism and Effect of Testosterone Therapy in Hypogonadal Men in Korea.
- Min Joo Kim, Jin Taek Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Sang Wan Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Kyong Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(3):225-231. Published online September 1, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.3.225
- 2,024 View
- 25 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
As the number of CAG repeats in the androgen receptor (AR) gene increases, transcriptional activities decrease and the effects of testosterone decline. In this study, we evaluated the importance of the CAG repeat polymorphism in regard to the effect/safety of testosterone therapy in hypogonadal Korean men. METHODS: The number of CAG repeats was determined in 42 hypogonadal men who underwent testosterone therapy for more than 24 months between December 1999 and August 2007. Body mass index, lean body mass, body fat, bone mineral density, type I collagen N-telopeptide (NTx), osteocalcin, lipid profile, hematocrit and PSA levels prior to and after 24 months of testosterone therapy were identified in our medical record review. RESULTS: Twenty-four months of testosterone therapy increased lean body mass, hematocrit, and PSA levels and reduced body fat, NTx, and HDL cholesterol levels. The mean number of CAG repeats in the AR gene was 23 +/- 3 (range, 15-29) in hypogonadal Korean men. The number of CAG repeats was not found to be associated with changes in lean body mass, body fat, NTx, HDL cholesterol, hematocrit, or PSA levels during testosterone therapy. CONCLUSIONS: No association between the number of CAG repeats in the AR gene and the effect/safety of testosterone therapy was detected in hypogonadal Korean men. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Androgen Receptor CAG Repeat Length as a Risk Factor of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in a Korean Male Population
Jong Wook Kim, Young Dae Bae, Sun Tae Ahn, Jin Wook Kim, Je Jong Kim, Du Geon Moon
Sexual Medicine.2018; 6(3): 203. CrossRef - Positive Correlation between Androgen Receptor CAG Repeat Length and Metabolic Syndrome in a Korean Male Population
Jong Wook Kim, Young Dae Bae, Sun Tae Ahn, Jin Wook Kim, Je Jong Kim, Du Geon Moon
The World Journal of Men's Health.2018; 36(1): 73. CrossRef - Genome-Based Approaches in Endocrinology and Metabolism: From Clinical and Research Aspects
Sihoon Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2011; 26(3): 208. CrossRef
- Androgen Receptor CAG Repeat Length as a Risk Factor of Late-Onset Hypogonadism in a Korean Male Population


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



